Connect AdjacentconnectAdjacent
The script connects points in a point cloud with polylines (primitives) based on the following rules:
- Points are connected if they are within a defined search radius (minSearchRadius-maxSearchRadius)
- Points are only connected if they belong to different classes
- Points are not connected if they are already neighbors
- If the targetPt attribute exists, connections are only made externally
- UseCase:
- Generating procedural geometry between points in a point cloud.
- Creating connections between points while respecting grouping (via the class attribute)
/*
Script: connectAdjacent
Version: 2.1
Author: Ceyhan Kapusuz
ver_1_0 01.06.2018
ver_2.0 27.11.2025 +codeCleanup
ver_2.1 01.2025 +refactoring and improvements
The script connectAdjacent connects points in a point cloud with polylines (primitives) based on the following rules:
Points are connected if they are within a defined search radius (minSearchRadius-maxSearchRadius)
Points are only connected if they belong to different classes
Points are not connected if they are already neighbors
If the targetPt attribute exists, connections are only made externally
UseCase:
Generating procedural geometry between points in a point cloud.
Creating connections between points while respecting grouping (via the class attribute)
*/
float minSearchRadius = ch("minSearchrad");
float maxSearchRadius = ch("maxSearchrad");
int maxConnections = chi("maxconnection");
int usePoints = chi("usePoints");
int createClassAttr = chi("createClassAttr");
int connectionCount = 0;
// Check if class attribute exists, create if missing
if (!haspointattrib(0, "class")) {
warning("Non-existent attribute: class. Creating class attribute from point number.");
i@class = @ptnum;
}
// Remove primitives if usePoints is enabled
if (usePoints) {
removeprim(0, @primnum, 0);
}
// Find nearby points within the search radius
int nearPts[] = nearpoints(0, @P, maxSearchRadius);
int neighborPts[] = neighbours(0, @ptnum);
int connectedPts[];
foreach (int npt; nearPts) {
// Skip if the point is itself, a neighbor, or in the same class
if (npt == @ptnum || npt == neighborPts[0] || npt == neighborPts[1]) {
continue;
}
int nearPointClass = point(0, "class", npt);
if (nearPointClass == @class) {
continue;
}
// Check if the point is already connected
int isAlreadyConnected = 0;
foreach (int connectedPt; connectedPts) {
if (npt == connectedPt) {
isAlreadyConnected = 1;
break;
}
}
if (!isAlreadyConnected) {
push(connectedPts, npt);
// Calculate distance between points
vector nptPos = point(0, "P", npt);
float dist = distance(@P, nptPos);
// Check minimum distance constraint and target point condition
if (dist > minSearchRadius && @targetPt == 0) {
int line = addprim(0, "polyline");
addvertex(0, line, @ptnum);
addvertex(0, line, npt);
// Store connection info
i@startPt = @ptnum;
i@endPt = npt;
connectionCount++;
// Stop if max connections reached
if (connectionCount >= maxConnections) {
break;
}
}
}
}
Scatter & instance tool.
Reads normal and tangent vectors, to create orient attribute .
This script is designed for controlling the instancing of objects along curves or surfaces in Houdini. It generates an @orient @pscale and @isntancepath attributes for each point to manage the scattering of instance objects.
Functionality:
- Gravity Application: Gravity is applied to the
@upvector, simulating a downward force. Usefull when instances branches or leaves. - Re-alignment: The
@up,@N, and@dirvectors are adjusted for correct orientation. - Density-Dependent Scaling: The scale of the scattered instances is adjusted based on the density of points.
- Rotation & Scale Control: Rotations are applied along the X, Y, and Z axes, with random offsets to create variation.
/*
Script: scatterOrientCtrl
Version: 3.6
ver_3_5 28.09.2021 rotate along with curve u attrib, pt remove func
ver 3.6 added normal lerp & fix on data type check on tangent attrib.
//function
scattered objects, rotation scale and instance control.
reads normal and tangent vectors, to create orient attribute .
*/
@id = @ptnum;
if (ch("removePt") >0)
{
if(@Cd.r<ch("removePt") )
removepoint(0,@ptnum);
}
//check to use up or tangentU
int upAttrExist = haspointattrib(0, "up");
int tangentUAttrExist = haspointattrib(0, "tangentu");
int NAttrExist = haspointattrib(0, "N");
if (upAttrExist ==0 && tangentUAttrExist ==1)
@up = v@tangentu;
if (tangentUAttrExist ==0 && upAttrExist ==0 )
{
warning("none existent attrb: tangentu or up ");
@up={1,0,0};
}
if (NAttrExist ==0)
{
warning("none existent attrb: N ");
@N={0,1,0};
}
//setInstancePath
string instancepath =("op:"+chs("instancepath"));
s@instancepath = instancepath;
//addForce
float gravity = (chf("gravity"));
vector gravityForce= {0, -1,0}*gravity;
float pushForce =(length(@force)*1);
@up += gravityForce;
@up= normalize(@up);
//reAlign directions
v@dir = cross(@N,@up);
//use scatter density dependent scale
float densityDependentScale= fit( @density, detail(0,"minDensity"), detail(0,"maxDensity"),(1-`chs("densityEffectScale")`),1 );
//randomScale
float scaleRand= fit01( rand(@ptnum+112), `chs("scaleRangex")`,`chs("scaleRangey")` );
//Cd effect Scale
float CdEffectScale = (ch('CdEffectScale'));
//calculate scale
float pScaleAlong = (chramp("pScaleAlong", @curveu));
@pscale = densityDependentScale * scaleRand * ((1-CdEffectScale)+(CdEffectScale*@Cd.r))* pScaleAlong ;
//use side effect on rotation
float sideEffectAngle = (ch('sideEffectAngle'));
@side += (1-sideEffectAngle);
//use surface alighment
//***************
v@N = normalize(lerp ({0,1,0},@N, sideEffectAngle));
v@dir = normalize(@dir);
v@up = normalize(@up);
float rotX_rand= (0.5-rand(@ptnum))*ch('rotX_rand')*12.6;
float rotY_rand= (0.5-rand(@ptnum))*ch('rotY_rand')*12.6;
float rotZ_rand= (0.5-rand(@ptnum))*ch('rotZ_rand')*6.3;
float rotX_mag= ch('rotX_mag')*6.3;
float rotY_mag= ch('rotY_mag')*6.3;
float rotZ_mag= ch('rotZ_mag')*6.3;
matrix3 m = maketransform( @up, @N);
float rotX = (chramp("rotX", @curveu)-0.5)*3.15;
float rotY = (chramp("rotY", @curveu)-0.5)*3.15;
float rotZ = (chramp("rotZ", @curveu)-0.5)*3.15;
float symX = ch('symX');
float symY = ch('symY');
float symZ = ch('symZ');
if (symX==0)
rotate(m, ( (rotX + rotX_mag + rotX_rand) *1 ), @N );
else
rotate(m, ( (rotX + rotX_mag + rotX_rand) *@side ), @N );
if (symY==0)
rotate(m, ( (rotY + rotY_mag + rotY_rand + pushForce) *1 ), @dir );
else
rotate(m, ( (rotY + rotY_mag + rotY_rand + pushForce) *@side ), @dir );
if (symY==0)
rotate(m, ( (rotZ + rotZ_mag + rotZ_rand) *1 ), @up );
else
rotate(m, ( (rotZ + rotZ_mag + rotZ_rand) *@side ), @up );
@orient = quaternion(m);
VectorOrtogonal
Function: Isolates the largest component of a vector, zeroes the other components,
and normalizes the result.
/*
Script: vectorOrtogonal
Version: 1.0
ver_1_0 27.11.2024
Function: Isolates the largest component of a vector, zeroes the other components,
and normalizes the result.
*/
vector inputVec = @N;
// Find the largest component
float maxComp = max(inputVec.x, max(inputVec.y, inputVec.z));
// Isolate the largest component and zero the others
if (inputVec.x == maxComp)
inputVec.y = inputVec.z = 0;
else if (inputVec.y == maxComp)
inputVec.x = inputVec.z = 0;
else
inputVec.x = inputVec.y = 0;
inputVec = normalize(inputVec); // Normalize
@N= inputVec;
RayProject
This script projects points onto a target geometry using ray intersection. Instead of projection, points can be tagged with attribute (Cd here). Similar functionality with ray sop, This script is used to create a mask for objects that are occluded from the camera’s view. It identifies cases where an object lies between the camera and the target surface,
/*
Script: Ray Projection
Version: 1.1
ver_1_0 27.11.2024 - Initial version
// Function: Projects points onto a target geometry using ray intersection.
// Updates point positions and colors based on the closest hit.
*/
// Get the target geometry (assume it's in the second input by default)
int target_geo = 1;
// Get the current point's position and normal
vector orig = @P;
vector dir = normalize(@N) * 1e6; // Scale the direction to a large distance
// Arrays to store intersection results
vector hit_positions[]; // Positions of the hits
int hit_prims[]; // Primitives hit
vector hit_uvs[]; // UV coordinates of the hits
float tol = 0.01; // Intersection tolerance
float ttol = 0.01; // Triangle tolerance
// Perform the ray intersection
int num_hits = intersect_all(target_geo, "", orig, dir, hit_positions, hit_prims, hit_uvs, tol, ttol);
// If there are hits, update the point position and color
if (num_hits > 0) {
// Initialize variables for the closest hit
float min_dist = distance(orig, hit_positions[0]);
vector closest_hit = hit_positions[0];
// Iterate over all hits to find the closest one
for (int i = 1; i < num_hits; i++) {
float dist = distance(orig, hit_positions[i]);
if (dist < min_dist) {
min_dist = dist;
closest_hit = hit_positions[i];
}
}
if(`ch("project")`==true){
// Update the point position to the closest hit position
@P = closest_hit;
}
// Color the point to indicate it was hit
@Cd = set(1, 0, 0); // Set the color to red
} else {
// Color the point to indicate no hit
@Cd = set(0, 0, 1); // Set the color to blue
}
CurveForce
Function: Applies directional, suction, orbital, and input forces along a curve. Uses ramps to control force influence based on curveu. Visualizes force influence using Cd. Usefull on pop curve force, or general force field generation.
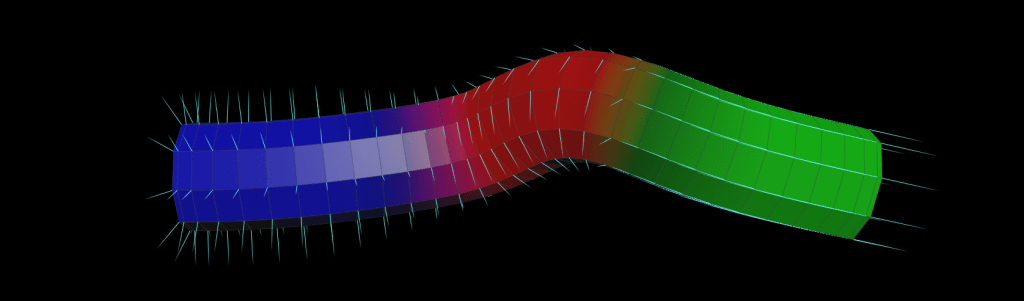
/*
Script: curveForce
Version: 1.3
Author: Ceyhan Kapusuz
ver_1_2 27.11.2024 - Initial version
ver_1_3 01.2025 - Refactored for clarity and robustness
// Function: Applies directional, suction, orbital, and input forces along a curve.
// Uses ramps to control force influence based on curveu.
// Visualizes force influence using Cd.
*/
// Ensure required attributes exist
if (!haspointattrib(0, "tangentu") || !haspointattrib(0, "N") || !haspointattrib(0, "curveu")) {
error("Missing required attributes: tangentu, N, or curveu.");
return;
}
// Define force directions
vector directionVelo = normalize(v@tangentu); // Direction along the curve
vector suctionVelo = normalize(v@N); // Suction direction (normal to the curve)
vector inputVelo = v@v * chf("inputV"); // Input velocity (scaled by parameter)
vector orbitalVelo = normalize(cross(@N, @tangentu)); // Orbital velocity (perpendicular to tangent and normal)
// Evaluate ramps based on curveu
float emissionAlong = chramp("emissionRamp", @curveu); // Emission influence
float directionAlong = chramp("directionalForceRamp", @curveu); // Directional force influence
float suctionAlong = chramp("suctionRamp", @curveu); // Suction force influence
float orbitalAlong = chramp("orbitalRamp", @curveu); // Orbital force influence
// Calculate force vectors
vector directionalVelocity = directionVelo * chf("directionalMag") * directionAlong;
vector suctionVelocity = suctionVelo * chf("suctionMag") * suctionAlong;
vector orbitalVelocity = orbitalVelo * chf("orbitalMag") * orbitalAlong;
// Combine forces and apply magnitude
v@v = (directionalVelocity + suctionVelocity + inputVelo + orbitalVelocity) * chf("magnitude");
// Calculate force (optional, if needed)
v@force = v@v * chf("forceMag");
// Visualize influence using Cd
@Cd.r = orbitalAlong; // Red channel: Emission influence
@Cd.g = directionAlong; // Green channel: Directional force influence
@Cd.b = suctionAlong; // Blue channel: Suction force influence
BlendControl
function: blend in given time range
user inputs for different blendTypes: 0=linear, 1=smooth step, 2=spline, 3=exponential, 4=logarithmic, and 5=sinusoidal transitions.
/*
Script: blendCtrl
Version: 1.0
Author: Ceyhan Kapusuz
ver_1_0 04.11.2019
//function
blend in given time range
0=linear, 1=smooth step, 2=spline, 3=exponential, 4=logarithmic, and 5=sinusoidal transitions.
*/
int blendStart = chi("blendStart");
int blendEnd = chi("blendEnd");
float startVal = ch("startVal");
float endVal = ch("endVal");
int transitionType = chi("transitionType");
float smoothRollOff = ch("smoothRollOff");
float transition = fit(@Frame, blendStart, blendEnd, 0, 1);
// Get the attribute name from the parameter
string attrName = chs("attributeName");
// Variable to hold the calculated value
float attrValue;
if (transitionType == 0) {
attrValue = lerp(startVal, endVal, transition); // Linear
} else if (transitionType == 1) {
attrValue = smooth(startVal, endVal, transition, smoothRollOff); // Smooth Step
} else if (transitionType == 2) {
attrValue = spline("catmull-rom", transition, startVal, endVal); // Spline
} else if (transitionType == 3) {
attrValue = startVal + (endVal - startVal) * pow(transition, 2.0); // Exponential
} else if (transitionType == 4) {
attrValue = startVal + (endVal - startVal) * log(1 + 9 * transition) / log(10); // Logarithmic
} else if (transitionType == 5) {
attrValue = startVal + (endVal - startVal) * (1 - cos(transition * M_PI)) / 2; // Sinusoidal
}
setattrib(0, "point",attrName, @ptnum,1,attrValue);
ForceGen
Function: Generates angular, central, and directional forces based on distance from a center point.
Provides visualization modes for debugging or artistic purposes. Usefull for generating positional and angular velocity for solvers
/*
Script: forceGen
Version: 1.1
ver_1_0 27.11.2024 - Initial version
ver_1_1 01.2025- cleanup & additional comments
// Function: Generates angular, central, and directional forces based on distance from a center point.
// Provides visualization modes for debugging or artistic purposes.
*/
// Get visualization mode
int visMode = chi("visMode");
// Get center point position
vector centerP = point(1, "P", 0);
// Define up vector and central vector
vector up = set(0, 1, 0);
vector centralVector = @P - centerP;
// Calculate distance from center and map it to a normalized range
float dist = length(centralVector);
float maxDist = chf("maxDist");
float distMapped = fit(dist, 0, maxDist, 1, 0);
// Calculate angular force
float distMappedAngular = chramp("dist_Angular", distMapped);
vector angularForce = cross(up, centralVector);
angularForce *= distMappedAngular * chf("angular_Mag");
// Calculate central force
float distMappedCentral = chramp("dist_Central", distMapped);
vector centralForce = centralVector * distMappedCentral * chf("central_Mag");
// Calculate directional force
float distMappedDirectional = chramp("dist_Directional", distMapped);
vector directionalForce = chv("directional") * distMappedDirectional * chf("directional_Mag");
// Apply global magnitude and Cd.r scaling
float globalMag = chf("globalMag") * @Cd.r;
// Accumulate forces
v@wForce += angularForce * globalMag;
v@vForce += (centralForce + directionalForce) * globalMag;
// Visualization modes
if (visMode == 0) {
@N = v@vForce * 1; // Visualize vForce
} else if (visMode == 1) {
@N = v@wForce * 0.2; // Visualize wForce
}
// Optional: Remove points with zero force (uncomment if needed)
// if (length(v@wForce) + length(v@vForce) == 0) {
// removepoint(0, @ptnum);
// }
