INDEX:
-noise&domainControl
-connectAdjacent
-scatter&instanceCOntrol
-vectorOrtagonal
-rayProject
-curveForce
-blendControl
-forceGen
noise&domain Control
Functionality: Script generates and controls various noise patterns applied to geometry in Houdini. It creates three distinct types of noise, blends or combines them, and outputs the result as the Cd attribute. Uses second inputs Cd or deformation attribute to deform noise space.
Parameters:
- type (int): The type of noise to generate (0 for Aligator, 1 for Perlin, 2 for Sparse Convolution, 3Worley noise. 4:Voronoi noise)
- deformDomain (float): Controls the amount of noise’s domain deformation. Instead of using @P uses (v@P + v@domainDeformation) for generation noise patern.
- deformation (vector): Specifies the deformation vector parameter. By default, it uses the
Cdattribute from the second input. - Noise1D: Determines the application of generated noise.
/*
Script: noiseCtrl
Version: 1.0
Overview and Functionality
Script generates and controls various noise patterns applied to geometry in Houdini.
It creates three distinct types of noise, blends or combines them, and outputs the result as the Cd attribute. Uses second inputs Cd or deformation attribute to deform noise space.
Parameters:
type (int): The type of noise to generate (0 for Aligator, 1 for Perlin, 2 for Sparse Convolution, 3Worley noise. 4:Voronoi noise.).
domainDeform (float): Controls the amount of noise's domain deformation. Instead of using @P uses (v@P + v@domainDeformV) for generation noise patern.
domainDeformV (vector): Specifies the deformation vector parameter. By default, it uses the Cd attribute from the second input.
Noise1D: Determines the application of generated noise.
*/
vector freq_A = chv("freq_A");
vector offset_A = chv("offset_A");
vector freq_B = chv("freq_B");
vector offset_B = chv("offset_B");
vector freq_C = chv("freq_C");
vector offset_C = chv("offset_C");
vector freq;
vector offset ;
//noisePrep
vector noiseType = chv("type_ABC");
float amp_A = chf("amp_A");
float rough_A = chf("roughness_A");
float atten_A = chf("attenuation_A");;
float turb_A = chf("turbulance_A");
float amp_B = chf("amp_B");
float rough_B = chf("roughness_B");
float atten_B = chf("attenuation_B");;
float turb_B = chf("turbulance_B");
float amp_C = chf("amp_C");
float rough_C = chf("roughness_C");
float atten_C = chf("attenuation_C");;
float turb_C = chf("turbulance_C");
float noiseGen(int type; vector position; vector freq; vector offset;float amp ;float rough; float atten; int turb; ) {
float resultNoise ;
vector jitter = set(1, 1,1); ;
vector noiseVal;
int seed;
float f1, f2, f3, f4;
vector pos1, pos2;
if (type==0)resultNoise = anoise((position * freq + offset ) , turb, rough, atten); //aligator
if (type==1)resultNoise = onoise((position * freq + offset ) , turb, rough, atten); //orig.Perline
if (type==2)resultNoise = snoise((position * freq + offset ) , turb, rough, atten); // Sparse Convolution
if (type == 3) {
wnoise((position * freq + offset ) , seed, f1, f2, f3, f4);
resultNoise = f1;
}
if (type == 4) {
vnoise( (position * freq + offset ) , jitter, seed, f1, f2, pos1, pos2);
pos1 = (pos1 - offset) / freq;
pos2 = (pos2 - offset) / freq;
float vnoise = f1;
resultNoise = f1;
}
resultNoise*=amp;
return resultNoise;
}
vector noiseVal;
int Noise1D = chi("Noise1D");
float domainDeform = chf("domainDeform");
vector domainDeformV ;
if (domainDeform>0){
domainDeformV = point(1,"Cd",@ptnum);
domainDeformV *= domainDeform;
}
if(Noise1D==0 || Noise1D==1 || Noise1D>3 ) noiseVal.x = noiseGen( noiseType.x , v@P+domainDeformV , freq_A , offset_A ,amp_A ,rough_A, atten_A, turb_A);
if(Noise1D==0 || Noise1D==2 || Noise1D>3 ) noiseVal.y = noiseGen( noiseType.y , v@P+domainDeformV , freq_B , offset_B ,amp_B ,rough_B, atten_B, turb_B);
if(Noise1D==0 || Noise1D==3 || Noise1D>3 ) noiseVal.z = noiseGen( noiseType.z , v@P+domainDeformV , freq_C , offset_C ,amp_C ,rough_C, atten_C, turb_C);
noiseVal.x = chramp("ramp_A",noiseVal.x);
noiseVal.y = chramp("ramp_B",noiseVal.y);
noiseVal.z = chramp("ramp_C",noiseVal.z);
if(Noise1D!=0){
if(Noise1D==1) noiseVal = noiseVal.x;
if(Noise1D==2) noiseVal = noiseVal.y;
if(Noise1D==3) noiseVal = noiseVal.z;
if(Noise1D==4) noiseVal = length(noiseVal);
if(Noise1D==5) noiseVal = (noiseVal.x*noiseVal.y*noiseVal.z);
}
@Cd = noiseVal ;
Connect Adjacent
The script connects points in a point cloud with polylines (primitives) based on the following rules:
- Points are connected if they are within a defined search radius (minSearchRadius-maxSearchRadius)
- Points are only connected if they belong to different classes
- Points are not connected if they are already neighbors
- If the targetPt attribute exists, connections are only made externally
- UseCase:
- Generating procedural geometry between points in a point cloud.
- Creating connections between points while respecting grouping (via the class attribute)
/*
Script: connectAdjacent
Version: 2.1
Author: Ceyhan Kapusuz
ver_1_0 01.06.2018
ver_2.0 27.11.2025 +codeCleanup
ver_2.1 01.2025 +refactoring and improvements
The script connectAdjacent connects points in a point cloud with polylines (primitives) based on the following rules:
Points are connected if they are within a defined search radius (minSearchRadius-maxSearchRadius)
Points are only connected if they belong to different classes
Points are not connected if they are already neighbors
If the targetPt attribute exists, connections are only made externally
UseCase:
Generating procedural geometry between points in a point cloud.
Creating connections between points while respecting grouping (via the class attribute)
*/
float minSearchRadius = ch("minSearchrad");
float maxSearchRadius = ch("maxSearchrad");
int maxConnections = chi("maxconnection");
int usePoints = chi("usePoints");
int createClassAttr = chi("createClassAttr");
int connectionCount = 0;
// Check if class attribute exists, create if missing
if (!haspointattrib(0, "class")) {
warning("Non-existent attribute: class. Creating class attribute from point number.");
i@class = @ptnum;
}
// Remove primitives if usePoints is enabled
if (usePoints) {
removeprim(0, @primnum, 0);
}
// Find nearby points within the search radius
int nearPts[] = nearpoints(0, @P, maxSearchRadius);
int neighborPts[] = neighbours(0, @ptnum);
int connectedPts[];
foreach (int npt; nearPts) {
// Skip if the point is itself, a neighbor, or in the same class
if (npt == @ptnum || npt == neighborPts[0] || npt == neighborPts[1]) {
continue;
}
int nearPointClass = point(0, "class", npt);
if (nearPointClass == @class) {
continue;
}
// Check if the point is already connected
int isAlreadyConnected = 0;
foreach (int connectedPt; connectedPts) {
if (npt == connectedPt) {
isAlreadyConnected = 1;
break;
}
}
if (!isAlreadyConnected) {
push(connectedPts, npt);
// Calculate distance between points
vector nptPos = point(0, "P", npt);
float dist = distance(@P, nptPos);
// Check minimum distance constraint and target point condition
if (dist > minSearchRadius && @targetPt == 0) {
int line = addprim(0, "polyline");
addvertex(0, line, @ptnum);
addvertex(0, line, npt);
// Store connection info
i@startPt = @ptnum;
i@endPt = npt;
connectionCount++;
// Stop if max connections reached
if (connectionCount >= maxConnections) {
break;
}
}
}
}
Scatter & instance tool.
Reads normal and tangent vectors, to create orient attribute .
This script is designed for controlling the instancing of objects along curves or surfaces in Houdini. It generates an @orient @pscale and @isntancepath attributes for each point to manage the scattering of instance objects.
Functionality:
- Gravity Application: Gravity is applied to the
@upvector, simulating a downward force. Usefull when instances branches or leaves. - Re-alignment: The
@up,@N, and@dirvectors are adjusted for correct orientation. - Density-Dependent Scaling: The scale of the scattered instances is adjusted based on the density of points.
- Rotation & Scale Control: Rotations are applied along the X, Y, and Z axes, with random offsets to create variation.
/*
Script: scatterOrientCtrl
Version: 3.6
ver_3_5 28.09.2021 rotate along with curve u attrib, pt remove func
ver 3.6 added normal lerp & fix on data type check on tangent attrib.
//function
scattered objects, rotation scale and instance control.
reads normal and tangent vectors, to create orient attribute .
*/
@id = @ptnum;
if (ch("removePt") >0)
{
if(@Cd.r<ch("removePt") )
removepoint(0,@ptnum);
}
//check to use up or tangentU
int upAttrExist = haspointattrib(0, "up");
int tangentUAttrExist = haspointattrib(0, "tangentu");
int NAttrExist = haspointattrib(0, "N");
if (upAttrExist ==0 && tangentUAttrExist ==1)
@up = v@tangentu;
if (tangentUAttrExist ==0 && upAttrExist ==0 )
{
warning("none existent attrb: tangentu or up ");
@up={1,0,0};
}
if (NAttrExist ==0)
{
warning("none existent attrb: N ");
@N={0,1,0};
}
//setInstancePath
string instancepath =("op:"+chs("instancepath"));
s@instancepath = instancepath;
//addForce
float gravity = (chf("gravity"));
vector gravityForce= {0, -1,0}*gravity;
float pushForce =(length(@force)*1);
@up += gravityForce;
@up= normalize(@up);
//reAlign directions
v@dir = cross(@N,@up);
//use scatter density dependent scale
float densityDependentScale= fit( @density, detail(0,"minDensity"), detail(0,"maxDensity"),(1-`chs("densityEffectScale")`),1 );
//randomScale
float scaleRand= fit01( rand(@ptnum+112), `chs("scaleRangex")`,`chs("scaleRangey")` );
//Cd effect Scale
float CdEffectScale = (ch('CdEffectScale'));
//calculate scale
float pScaleAlong = (chramp("pScaleAlong", @curveu));
@pscale = densityDependentScale * scaleRand * ((1-CdEffectScale)+(CdEffectScale*@Cd.r))* pScaleAlong ;
//use side effect on rotation
float sideEffectAngle = (ch('sideEffectAngle'));
@side += (1-sideEffectAngle);
//use surface alighment
//***************
v@N = normalize(lerp ({0,1,0},@N, sideEffectAngle));
v@dir = normalize(@dir);
v@up = normalize(@up);
float rotX_rand= (0.5-rand(@ptnum))*ch('rotX_rand')*12.6;
float rotY_rand= (0.5-rand(@ptnum))*ch('rotY_rand')*12.6;
float rotZ_rand= (0.5-rand(@ptnum))*ch('rotZ_rand')*6.3;
float rotX_mag= ch('rotX_mag')*6.3;
float rotY_mag= ch('rotY_mag')*6.3;
float rotZ_mag= ch('rotZ_mag')*6.3;
matrix3 m = maketransform( @up, @N);
float rotX = (chramp("rotX", @curveu)-0.5)*3.15;
float rotY = (chramp("rotY", @curveu)-0.5)*3.15;
float rotZ = (chramp("rotZ", @curveu)-0.5)*3.15;
float symX = ch('symX');
float symY = ch('symY');
float symZ = ch('symZ');
if (symX==0)
rotate(m, ( (rotX + rotX_mag + rotX_rand) *1 ), @N );
else
rotate(m, ( (rotX + rotX_mag + rotX_rand) *@side ), @N );
if (symY==0)
rotate(m, ( (rotY + rotY_mag + rotY_rand + pushForce) *1 ), @dir );
else
rotate(m, ( (rotY + rotY_mag + rotY_rand + pushForce) *@side ), @dir );
if (symY==0)
rotate(m, ( (rotZ + rotZ_mag + rotZ_rand) *1 ), @up );
else
rotate(m, ( (rotZ + rotZ_mag + rotZ_rand) *@side ), @up );
@orient = quaternion(m);
VectorOrtogonal
Function: Isolates the largest component of a vector, zeroes the other components,
and normalizes the result.
/*
Script: vectorOrtogonal
Version: 1.0
ver_1_0 27.11.2024
Function: Isolates the largest component of a vector, zeroes the other components,
and normalizes the result.
*/
vector inputVec = @N;
// Find the largest component
float maxComp = max(inputVec.x, max(inputVec.y, inputVec.z));
// Isolate the largest component and zero the others
if (inputVec.x == maxComp)
inputVec.y = inputVec.z = 0;
else if (inputVec.y == maxComp)
inputVec.x = inputVec.z = 0;
else
inputVec.x = inputVec.y = 0;
inputVec = normalize(inputVec); // Normalize
@N= inputVec;
RayProject
This script projects points onto a target geometry using ray intersection. Instead of projection, points can be tagged with attribute (Cd here). Similar functionality with ray sop, This script is used to create a mask for objects that are occluded from the camera’s view. It identifies cases where an object lies between the camera and the target surface,
/*
Script: Ray Projection
Version: 1.1
ver_1_0 27.11.2024 - Initial version
// Function: Projects points onto a target geometry using ray intersection.
// Updates point positions and colors based on the closest hit.
*/
// Get the target geometry (assume it's in the second input by default)
int target_geo = 1;
// Get the current point's position and normal
vector orig = @P;
vector dir = normalize(@N) * 1e6; // Scale the direction to a large distance
// Arrays to store intersection results
vector hit_positions[]; // Positions of the hits
int hit_prims[]; // Primitives hit
vector hit_uvs[]; // UV coordinates of the hits
float tol = 0.01; // Intersection tolerance
float ttol = 0.01; // Triangle tolerance
// Perform the ray intersection
int num_hits = intersect_all(target_geo, "", orig, dir, hit_positions, hit_prims, hit_uvs, tol, ttol);
// If there are hits, update the point position and color
if (num_hits > 0) {
// Initialize variables for the closest hit
float min_dist = distance(orig, hit_positions[0]);
vector closest_hit = hit_positions[0];
// Iterate over all hits to find the closest one
for (int i = 1; i < num_hits; i++) {
float dist = distance(orig, hit_positions[i]);
if (dist < min_dist) {
min_dist = dist;
closest_hit = hit_positions[i];
}
}
if(`ch("project")`==true){
// Update the point position to the closest hit position
@P = closest_hit;
}
// Color the point to indicate it was hit
@Cd = set(1, 0, 0); // Set the color to red
} else {
// Color the point to indicate no hit
@Cd = set(0, 0, 1); // Set the color to blue
}
CurveForce
Function: Applies directional, suction, orbital, and input forces along a curve. Uses ramps to control force influence based on curveu. Visualizes force influence using Cd. Usefull on pop curve force, or general force field generation.
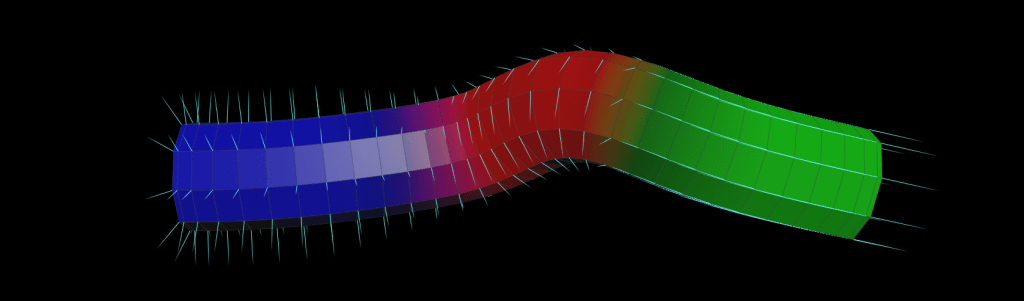
/*
Script: curveForce
Version: 1.3
Author: Ceyhan Kapusuz
ver_1_2 27.11.2024 - Initial version
ver_1_3 01.2025 - Refactored for clarity and robustness
// Function: Applies directional, suction, orbital, and input forces along a curve.
// Uses ramps to control force influence based on curveu.
// Visualizes force influence using Cd.
*/
// Ensure required attributes exist
if (!haspointattrib(0, "tangentu") || !haspointattrib(0, "N") || !haspointattrib(0, "curveu")) {
error("Missing required attributes: tangentu, N, or curveu.");
return;
}
// Define force directions
vector directionVelo = normalize(v@tangentu); // Direction along the curve
vector suctionVelo = normalize(v@N); // Suction direction (normal to the curve)
vector inputVelo = v@v * chf("inputV"); // Input velocity (scaled by parameter)
vector orbitalVelo = normalize(cross(@N, @tangentu)); // Orbital velocity (perpendicular to tangent and normal)
// Evaluate ramps based on curveu
float emissionAlong = chramp("emissionRamp", @curveu); // Emission influence
float directionAlong = chramp("directionalForceRamp", @curveu); // Directional force influence
float suctionAlong = chramp("suctionRamp", @curveu); // Suction force influence
float orbitalAlong = chramp("orbitalRamp", @curveu); // Orbital force influence
// Calculate force vectors
vector directionalVelocity = directionVelo * chf("directionalMag") * directionAlong;
vector suctionVelocity = suctionVelo * chf("suctionMag") * suctionAlong;
vector orbitalVelocity = orbitalVelo * chf("orbitalMag") * orbitalAlong;
// Combine forces and apply magnitude
v@v = (directionalVelocity + suctionVelocity + inputVelo + orbitalVelocity) * chf("magnitude");
// Calculate force (optional, if needed)
v@force = v@v * chf("forceMag");
// Visualize influence using Cd
@Cd.r = orbitalAlong; // Red channel: Emission influence
@Cd.g = directionAlong; // Green channel: Directional force influence
@Cd.b = suctionAlong; // Blue channel: Suction force influence
BlendControl
function: blend in given time range
user inputs for different blendTypes: 0=linear, 1=smooth step, 2=spline, 3=exponential, 4=logarithmic, and 5=sinusoidal transitions.
/*
Script: blendCtrl
Version: 1.0
Author: Ceyhan Kapusuz
ver_1_0 04.11.2019
//function
blend in given time range
0=linear, 1=smooth step, 2=spline, 3=exponential, 4=logarithmic, and 5=sinusoidal transitions.
*/
int blendStart = chi("blendStart");
int blendEnd = chi("blendEnd");
float startVal = ch("startVal");
float endVal = ch("endVal");
int transitionType = chi("transitionType");
float smoothRollOff = ch("smoothRollOff");
float transition = fit(@Frame, blendStart, blendEnd, 0, 1);
// Get the attribute name from the parameter
string attrName = chs("attributeName");
// Variable to hold the calculated value
float attrValue;
if (transitionType == 0) {
attrValue = lerp(startVal, endVal, transition); // Linear
} else if (transitionType == 1) {
attrValue = smooth(startVal, endVal, transition, smoothRollOff); // Smooth Step
} else if (transitionType == 2) {
attrValue = spline("catmull-rom", transition, startVal, endVal); // Spline
} else if (transitionType == 3) {
attrValue = startVal + (endVal - startVal) * pow(transition, 2.0); // Exponential
} else if (transitionType == 4) {
attrValue = startVal + (endVal - startVal) * log(1 + 9 * transition) / log(10); // Logarithmic
} else if (transitionType == 5) {
attrValue = startVal + (endVal - startVal) * (1 - cos(transition * M_PI)) / 2; // Sinusoidal
}
setattrib(0, "point",attrName, @ptnum,1,attrValue);
ForceGen
Function: Generates angular, central, and directional forces based on distance from a center point.
Provides visualization modes for debugging or artistic purposes. Usefull for generating positional and angular velocity for solvers
/*
Script: forceGen
Version: 1.1
ver_1_0 27.11.2024 - Initial version
ver_1_1 01.2025- cleanup & additional comments
// Function: Generates angular, central, and directional forces based on distance from a center point.
// Provides visualization modes for debugging or artistic purposes.
*/
// Get visualization mode
int visMode = chi("visMode");
// Get center point position
vector centerP = point(1, "P", 0);
// Define up vector and central vector
vector up = set(0, 1, 0);
vector centralVector = @P - centerP;
// Calculate distance from center and map it to a normalized range
float dist = length(centralVector);
float maxDist = chf("maxDist");
float distMapped = fit(dist, 0, maxDist, 1, 0);
// Calculate angular force
float distMappedAngular = chramp("dist_Angular", distMapped);
vector angularForce = cross(up, centralVector);
angularForce *= distMappedAngular * chf("angular_Mag");
// Calculate central force
float distMappedCentral = chramp("dist_Central", distMapped);
vector centralForce = centralVector * distMappedCentral * chf("central_Mag");
// Calculate directional force
float distMappedDirectional = chramp("dist_Directional", distMapped);
vector directionalForce = chv("directional") * distMappedDirectional * chf("directional_Mag");
// Apply global magnitude and Cd.r scaling
float globalMag = chf("globalMag") * @Cd.r;
// Accumulate forces
v@wForce += angularForce * globalMag;
v@vForce += (centralForce + directionalForce) * globalMag;
// Visualization modes
if (visMode == 0) {
@N = v@vForce * 1; // Visualize vForce
} else if (visMode == 1) {
@N = v@wForce * 0.2; // Visualize wForce
}
// Optional: Remove points with zero force (uncomment if needed)
// if (length(v@wForce) + length(v@vForce) == 0) {
// removepoint(0, @ptnum);
// }